|
How Does Reverse Osmosis
Work?
Reverse osmosis systems purify water by forcing pressurized
water through a very fine, plastic membrane.
Stages of reverse osmosis:
-
During the
initial filtration stage, tap water or well water
(pressurized by a booster pump) is passed through
a particle filter (a pre-filter) that removes silt,
sediment, sand, and clay particles that might clog
the R/O membrane.
-
The water
is then forced through an activated carbon filter
that traps minerals and contaminants such as chromium,
mercury, copper, chloramine and pesticides. It also
removes chlorine, which is important, as chlorine
will shorten the life of the membrane.
-
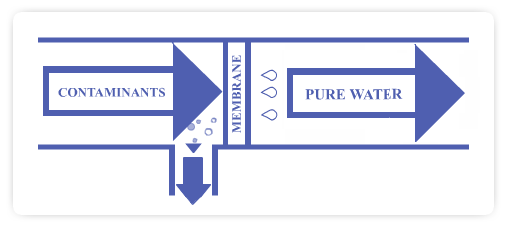
Water is
transferred under pressure into the R/O module,
allowing only clean water to pass through the small
pores in the membrane. Impurities unable to pass
through the membrane are left behind and flushed
down the drain.
-
Treated water
is then sent to a storage-tank. Treated
water is passed through an activated carbon filter
before use to further improve the water's taste
and smell.
What Are the
Benefits of Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis can remove dissolved solids, salts,
minerals that cause hardness, organic chemicals and
other impurities. It can improve the taste of water
for people who do not like the taste of dissolved mineral
solids. Treated water will not produce scale in kettles
and coffee makers. Because sodium and potassium are
removed, people on a medically prescribed sodium- or
potassium-restricted diet may benefit. R/O units also
remove contaminants such as chromium, mercury and nitrates.
In addition, reverse osmosis removes fluoride.
Is Reverse Osmosis - Treated Water Safe to Drink?
Reverse osmosis treatment systems remove minerals like
calcium and magnesium from drinking water. In Canada,
water is a minor source of such minerals when compared
to foods. If you consume a reasonably balanced diet,
you do not need to take a mineral supplement when drinking
water treated with a reverse osmosis system.
Additional Information
Reverse osmosis is a scientific application
where dissolved contaminants in water are physically
removed by passing it under pressure through a special
membrane. The process is similar to the way your body’s
cells absorb water. Reverse osmosis will remove up to
98% of dissolved contaminants such as minerals, salts,
metals and organic matter that may be present in a water
supply. Pores in the reverse osmosis membrane are so
small that only water molecules can make it through
and the contaminants that are not recognized by the
membrane are rejected and flushed down the drain. By
way of example the pores of the reverse osmosis membrane
are 0.0006 microns. A common bacteria is from 0.4 –
1.0 microns, a virus is from 0.2 – 0.4 microns
and dissolved sugar is 0.001 – 0.005 microns.
So it’s easy to understand why they just don’t
make the passing grade.
The following shows the rejection
rate of only a few of the commonly found dissolved solids
in drinking water.
| Dissolved Solids |
Removal Rate |
Dissolved Solids |
Removal Rate |
| Aluminium |
99% |
Nitrate |
97% |
| Bacteria |
99% |
Pesticides |
99% |
| Chloride |
99% |
Polyphosphate |
99% |
| Iron |
99% |
Radium |
98% |
| Lead |
99% |
Sodium |
96% |
| Mercury |
97% |
Zinc |
96% |
Information obtained from (CMHC)
Canada Housing and Mortgage Corporation and Health Canada
and other industry sources.
|


